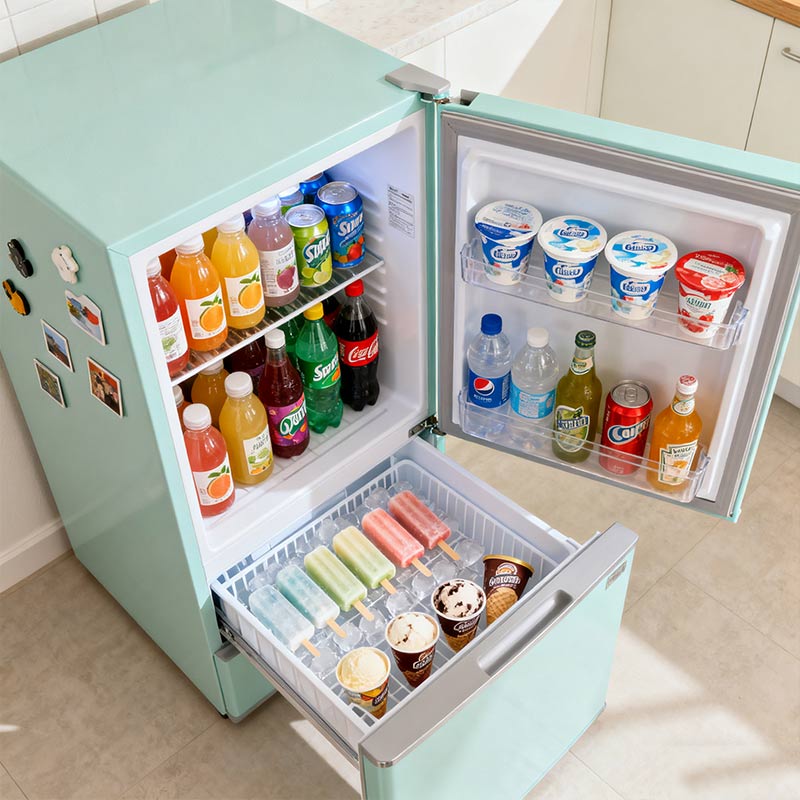
The cooling principle of an air-cooled refrigerator is similar to the "blowing air to cool down" of an air conditioner. In simple terms, the evaporator is hidden inside the refrigerator, and the cold air is blown to every corner by the fan for continuous cooling. When the temperature in the refrigerator compartment or freezer rises, the fan automatically starts to quickly circulate the cold air into the room, bringing the temperature back to the set value. It's like installing a small "air circulation system" inside the refrigerator. Constantly supply cold air to the food.

The direct-cooling refrigerator is like a "silent refrigeration craftsman", using refrigerant to directly cool the interior of the refrigerator. The refrigerant absorbs heat on the surface of the evaporator to achieve cooling. The evaporator is usually composed of S-shaped cold coil tubes, which directly contact the inner wall of the freezing chamber for heat exchange. This direct contact cooling method makes the direct-cooling ice box quieter when cooling.
What is the difference between automatic defrosting and manual defrosting?
Air-cooled refrigerators are known for being "frost-free", but in fact, frost forms on the evaporator. After the refrigerator has been working for a period of time (usually about 8 hours), it will stop cooling and start the defrosting heating system. The frost turns into water when heated and is discharged through a dedicated pipe (or directly evaporates into water vapor). The entire process is completed automatically without the need for manual handling by the user. However, there may occasionally be a few water droplets in the fresh-keeping compartment of an air-cooled refrigerator.
Due to high air humidity, the surface of the evaporator in direct-cooling refrigerators is prone to frost formation. Over time, thick ice layers may form on the rear wall of the refrigerator compartment. At this point, users need to cut off the power, empty the refrigerator, and use a shovel to remove the ice. This is not only laborious but may also damage the inner wall. Moreover, frost formation can affect the cooling efficiency and storage space.

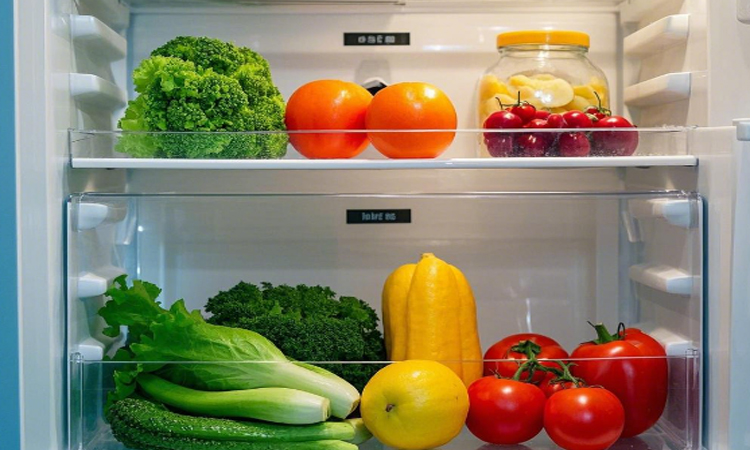
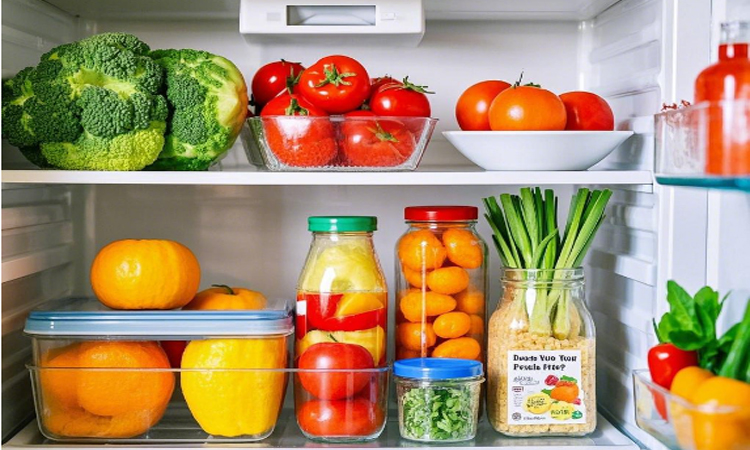
In terms of preservation, due to the lack of cold air circulation in direct-cooling refrigerators, the humidity is relatively high, making them suitable for storing fruits and vegetables, as they can keep food in a fresh and juicy state. However, their temperature is uneven; areas close to the evaporator may be too cold and freeze food, while areas far away may not be cold enough, causing food to spoil easily.